Cannabis provides several significant therapeutic benefits. Depending on the strain you use, it can help you to relax, feel more energized, alleviate pain, or reduce anxiety. It can help with a wide variety of medical conditions, including arthritis, cancer, epilepsy, and more. Cannabinoids play a significant role in the benefits you experience when using cannabis. But what are cannabinoids? Here’s what you need to know.
What Are Cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are naturally-occurring compounds in the cannabis plant. They’re a major component of what provides you with the effects you feel when you smoke, vape, or eat an edible. Certain cannabinoids, such as THC, also lead to the high typically associated with the plant.
How Cannabinoids Work
Cannabinoids interact with the endocannabinoid system within your body by bonding with cannabinoid (CB) receptors. These receptors are found in your brain and throughout your body, including your digestive system, spinal cord, and various organs. They’re also in your skin.
There are two types of CB receptors, CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are mainly in the brain and spinal cord, while CB2 receptors are mainly in the immune system and other places throughout your body.
When cannabinoids bind with the receptors, they “unlock” them to produce certain effects. What’s interesting is that different cannabinoids produce different effects based on which receptors they bind to and where those receptors are in the body.
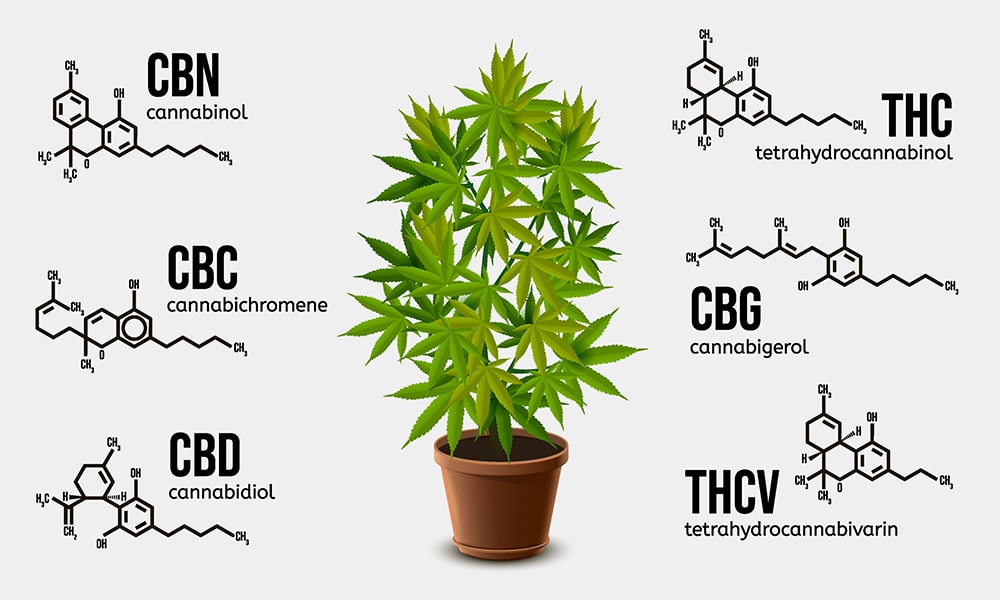
Common Cannabinoids in Cannabis
Researchers have identified over 100 cannabinoids, which are unique to the cannabis plant. Different strains contain different cannabinoids in different amounts. Some cannabinoids are more common than others. Here are some of the most common ones you’ll find:
THC. THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is one of the most well-known cannabinoids. It’s the one that’s responsible for the high most people associate with the cannabis plant. In addition to the high, it can help users to feel more relaxed and happy. It can also help alleviate pain and help treat symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, sleep apnea, and more.
CBD. CBD (cannabidiol) is another well-known cannabinoid. It does not produce any psychoactive effects. Where THC binds to CB1 receptors, CBD typically binds to CB2. While it doesn’t get you high, it can still help to reduce anxiety and improve sleep quality.
CBN. CBN (cannabinol) has some psychoactive effects, but these effects aren’t nearly as strong as THC. It’s actually a byproduct of THC, and it only develops when THC is exposed to oxygen. While it’s effects are still being researched, it appears to be beneficial for improving sleep.
CBC. Another non-psychoactive cannabinoid, CBC (cannabichromene) can help to counteract the effects of THC, similar to CBD. It may also help with neuroplasticity, which refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize itself and form new neural connections to compensate for disease or injury.
CBG. CBG (cannabigerol) isn’t as common as some of the previously mentioned cannabinoids, but it’s still becoming a subject of interest for researchers. While only present in small amounts and non-psychoactive, it shows promise to help with conditions such as Crohn’s disease, IBS, cancerous tumors, and glaucoma.
What Are Cannabinoids & Why You Should Care
Cannabinoids play a significant role in the effects you experience when you use a specific cannabis product. Understanding the cannabinoid content of a certain strain or product can help you choose one that best suits your needs and goals.